Hypothyroidism is a condition where your thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough of certain hormones thereby upsetting the normal balance of chemical processes in your body. The thyroid releases the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) by which the metabolism of most of your body’s organs is determined. The gland is regulated by the thyroid stimulating hormone made by the pituitary gland.
When the thyroid gland becomes underactive (hypothyroidism), problems occur and this condition is more common in women than men. However, rest assured, there are diagnostic tests and treatment options to help you lead a normal life without hypothyroidism affecting your quality of life.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Thyroid related diseases occur due to imbalanced TSH levels, or problems in the thyroid gland. Causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis – an autoimmune condition where antibodies made by the body destroy parts of the thyroid gland.
- Certain medications – Amiodarone etc.
- Pituitary Problems
- Hypothalamus problems
- Iodine deficiency
- Babies born with congenital hypothyroidism
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
The symptoms vary according to the severity of the deficiency. Initially, it’s very hard to notice the symptoms and the general symptoms like weight gain and hair thinning are hardly noticeable. However, over time you may start noticing other symptoms as shown below. Some of the common symptoms include:
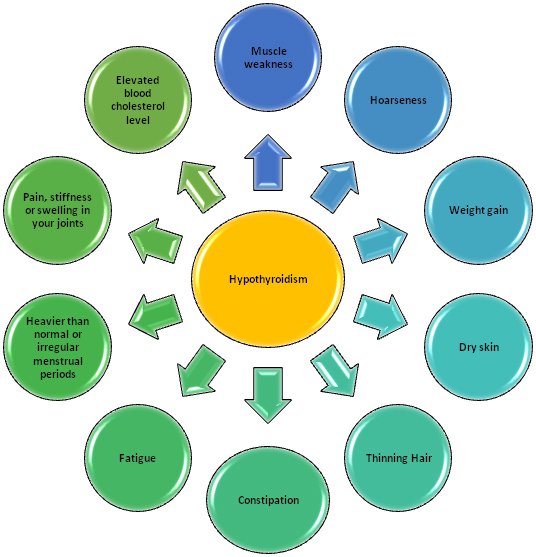
Other severe symptoms include slowed heart rate, poor memory, depression etc.
When hypothyroidism isn’t treated, it could lead to an enlarged thyroid called goiter. An advanced form of hypothyroidism, which is extremely rare called myxedema is life-threatening. Symptoms include low blood pressure, decreased body temperature, unresponsiveness, unresponsiveness, and coma. It can sometimes be fatal.
When should you see a Doctor?
If you experience any of the above signs for an extended period of time, it’s time to see a doctor. You should also test your thyroid function periodically in case you’ve had surgery, been treated with anti-thyroid medications or radiation therapy in your head, neck or chest. In case you have high blood pressure or are receiving hormone therapy for hypothyroidism, it’s important to make follow up visits for checking your thyroid levels and adjusting the correct dosage of medicines.
Diagnosis
Hypothyroidism can be confirmed by laboratory tests which measure the levels of TSH and thyroid hormone. Serology tests can also measure the antibodies associated with hypothyroidism.
Treatment for Hypothyroidism
The usual treatment for hypothyroidism is Thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Here, synthetic thyroid hormone is taken orally to replace the thyroid hormone and this is lifelong usually.
Pregnant women need to increase their thyroid replacement by 50%. It takes 4 to 6 weeks for the effect of the therapy to be reflected. The medications reverse any weight gain and high cholesterol gained by hypothyroidism. To determine the right dosage your body needs, the doctor checks your TSH after a couple of months. In case of coronary heart disease and severe hypothyroidism, the treatment is started on a smaller dosage and gradually increased.
Diet for Hypothyroidism
Generally, there’s no fixed diet for hypothyroidism, there’s no evidence that certain foods like cabbage can alter your thyroid function. Make sure your diet has adequate iodine to ensure proper thyroid function. Ensure you take a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and pulses.
With proper care, you can lead a normal life even with hypothyroidism. Make sure you have followed up visits to ensure your thyroid hormones are at the right levels.



